Material handling equipment is any machine or tool that is used to transport, process, store, or package materials. For example, forklifts, conveyors, shelves, and even autonomous mobile robots (AMRs).
Using material handling equipment improves efficiency and can help automate processes that would otherwise require a lot of manual labor, saving you time and money. Common uses for material handling equipment include processing agricultural products like grain, organizing and storing inventory in a warehouse, and loading and unloading dirt or hardscape.
In this post, we go over the four material handling categories and the equipment within each category, so you can choose the right tools for your workflow.
4 Categories of Material Handling Equipment
The four main categories of material handling equipment are storage and handling equipment, industrial trucks, bulk material handling equipment, and engineered systems.
This chart breaks down the common uses and tools for each category:
| Storage and Handling Equipment | Industrial Trucks and Machines | Bulk Material Handling Equipment | Engineered Systems | |
| Used for | Storage and inventory, organization, and preparation | Transporting materials to a designated area | Storing, transporting, or processing materials in bulk | Packaging, shelving, or storing materials |
| Type of tools | Shelves, storage racks, and mezzanines | Forklifts, order pickers, and pallet jacks | Conveyors, hoppers, and reclaimers | Palletizers, automated guided vehicles, and warehouse robots |
Storage and Handling Equipment
Storage and handling equipment is the most basic of the four categories. As the name implies, it is used to store products that are being held as inventory or materials that are awaiting the next part of the production process. This equipment helps you maximize your space, particularly your vertical and floor space.
Common types of storage equipment include:
- Bins and drawers: These hold small to medium-sized items. Bins have open tops, allowing employees or automated systems to quickly grab inventory. Drawers allow for high-density storage and may maximize space better than shelves.
- Mezzanines: Mezzanines are semi-permanent structures that add another floor between the floor and the ceiling. This increases a warehouse’s usable space, providing additional workspace or a larger storage area.
- Pallets: Pallets store packaged loads, making it easier to move and transport them with industrial trucks or pallet jacks.
- Pallet stacking frames: These attach to pallets, allowing you to stack palletized loads on top of each other. They require minimal storage space when they’re not being used.
- Storage containers: Storage containers, also called shipping containers, can come in a variety of sizes, but are generally designed to store large objects or large amounts of materials.
- Storage racks: Similar to shelving, storage or pallet racks help teams make use of their vertical space by providing several horizontal platforms. Drive-in racks allow forklifts to drive in and load pallets, increasing storage space, but minimizing accessibility.
Industrial Trucks and Machines
These machines are used to load and transport materials. They can be manual, like hand trucks, or motorized, like forklifts. Industrial trucks primarily use fork attachments, which are compatible with palletized loads.
The most common types of industrial trucks for material handling are:
- Forklifts: Most standard warehouse forklifts can handle loads up to 5,000 pounds and lift 10 to 15 feet. Large-capacity models can carry much heavier loads.
- Order pickers: Order pickers raise warehouse employees, allowing them to pick orders off of elevated shelves. Their load capacity is typically around 3,000 pounds and they can raise up to 32 feet.
- Pallet jacks: Also known as pallet trucks, these machines come in manual and electric versions. They typically only transport one to two pallets at a time and their load capacity maxes out around 5,500 pounds for standard models, though you can also find high-capacity options.
- Side loaders: These are a type of forklift with forks at the side instead of the front. This allows the machine to navigate in narrow aisles, like between warehouse shelving, and load products without turning the cab.
- Walkie stackers: Walkie stackers don’t have a cab – the operator stands behind the machine while operating it. Similar to pallet jacks, walkie stackers have a limited load capacity, ranging from 2,000 to 4,000 pounds. They can typically lift 5 to 10 feet.
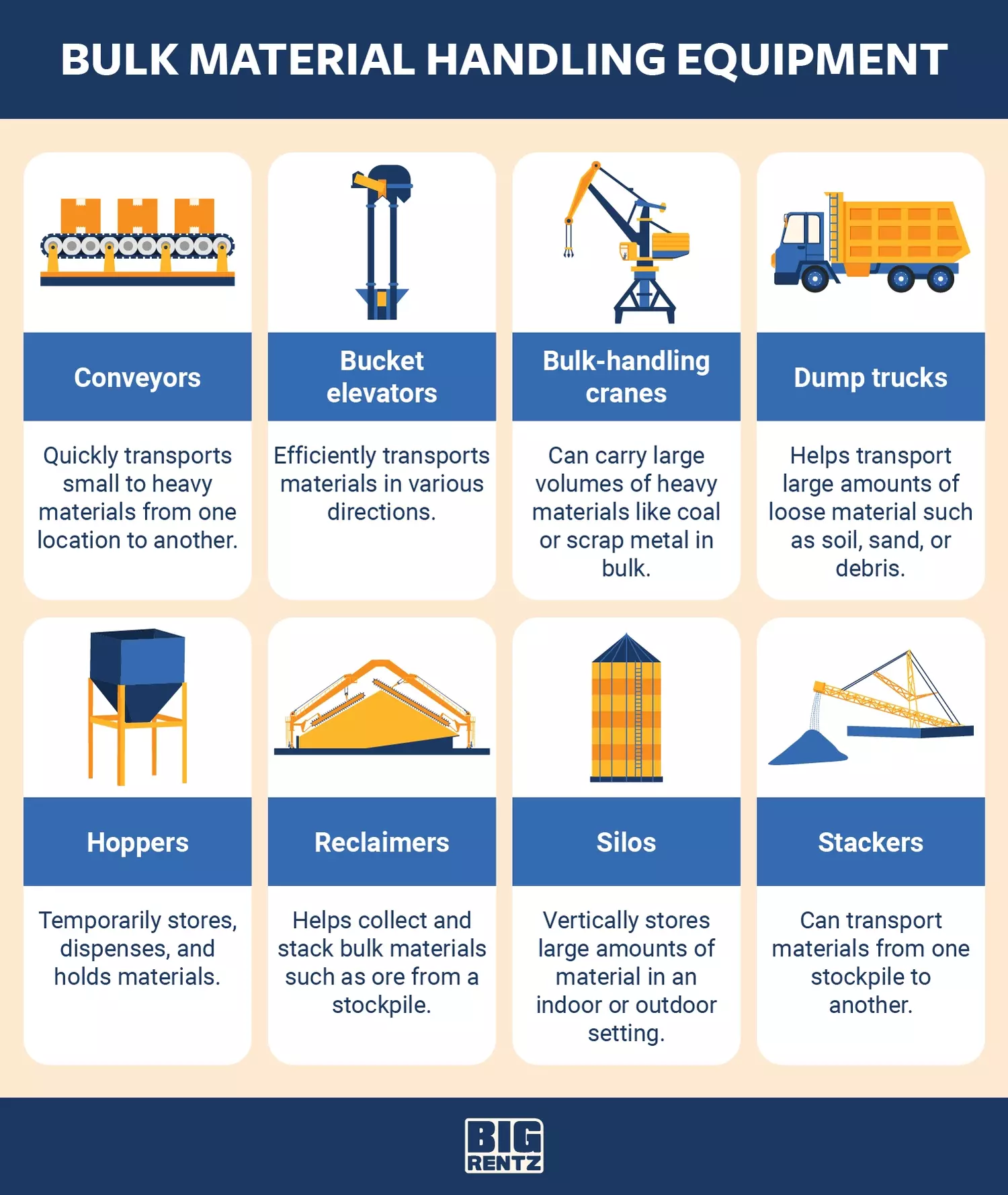
Bulk Material Handling Equipment
Bulk material handling equipment helps to move, load, and process large quantities of items. This includes small items like grain or rocks, and larger items like consumer packaged goods.
You may find this equipment in indoor and outdoor environments. For example, silos may store bulk food items on a farm and conveyors transport packages in a warehouse.
Common types of bulk material handling equipment include:
- Conveyors: A conveyor system helps move and process materials en masse. Similar to an old-school assembly line, it uses a system of belts and pulleys to keep things moving from point A to point B.
- Bucket elevators: A bucket elevator, also called a grain leg or grain elevator, hauls flowable bulk materials vertically. It’s typically used in an agricultural setting, moving loose materials like grain or fertilizer.
- Bulk-handling cranes: Building on the design of a basic crane, a bulk-handling crane includes a two-piece hinged grab to lift and balance bulk cargo like coal or mineral ore.
- Dump trucks: A dump truck is a vehicle designed for transporting and unloading large quantities of materials. It’s often used in construction to offload or haul away debris or loose materials.
- Hoppers: Often used in agriculture, hoppers are containers that transport bulk products like grain and corn, unloading them through compartments at the bottom.
- Stackers and reclaimers: A reclaimer is typically used in conjunction with a stacker. The stacker piles bulk material like ore or coal. The reclaimer loads it, guiding it to a conveyor to be transported.
- Silos: Silos are tall, cylindrical containers that provide high-volume storage for items like coal, woodchips, or feed.
Engineered Systems
Engineered systems are completely automated. As the name implies, they use multiple systems to minimize the need for manual labor. This type of material handling equipment is commonly found in manufacturing and warehousing.
These are some of the most common engineered systems:
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (AR/RS): AR/RS is a type of robotic delivery system that can place and retrieve materials from set storage locations.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGV): Sometimes called self-guided vehicles, AGVs are designed to drive and operate themselves, following marked lines, wires in the floor, or other programmed controls for navigation.
- Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs): AMRs are more advanced than AVGs. They can map and adapt to their surroundings using sensors.
- Palletizers: Palletizers replace the need for humans to load pallets. They stack items on a pallet and release the pallet onto a conveyor for further processing.
- Sortation systems: Sortation systems can automatically detect objects and route them to the desired location.
- Warehouse robots: Warehouse robots are AI designed for use in warehouse applications to automate simple, repetitive tasks, like picking products off of a shelf.
How to Choose Material Handling Equipment
As you can see, there are many different types of material handling equipment to assist with manufacturing, warehousing, agricultural, or construction needs. Choosing the right piece of equipment depends on a variety of factors.
Function and Space
The purpose of material handling equipment is to improve efficiency. Consider how you can productively use all your space. For example, you may want to add a mezzanine to a warehouse to increase your square footage.
The Type of Materials
The size and shape of your material will dictate the type of material handling equipment you need. Granular items may need to be packaged, while boxed items can easily be palletized.
If you’re working in an outdoor environment, you may require a crane to move large, heavy materials or a reclaimer to sift through stockpiles.
Automation vs. Labor
Automation increases efficiency, but it comes at a cost. You’ll likely use a combination of automated and manual equipment. For example, robotic delivery systems may pick products in a warehouse and deliver them to a human for quality assurance and packaging.
Need to Rent Out Material Handling Equipment?
If you require industrial trucks for your job, BigRentz has a variety of material handling equipment for rent, including forklifts, pallet jacks, and walkie stackers. Our warehouse forklifts range in capacity from 5,000 pounds to 25,000 pounds, so, no matter what you’re moving, we have you covered.